 Water Related
Water Related
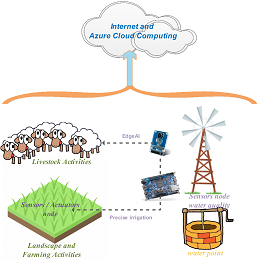
Smart water monitoring, protection of pastoral and agricultural areas on dry-lands
EM005 »
With climate change and water scarcity, arid countries' policies aim to conserve dams’ water for domestic and industrial use only. Due to a lack of budget, having no other alternative, Small-farms crop production turns to the use of innovative low-cost solutions for irrigation and livestock. The proposed project outlines a new approach supporting agricultural agencies and policies at all levels, livestock professionals, smallholding farmers, and local populations, to stabilize the ecologically unsustainable exploitation of the water on dry-lands. The proposed approaches aim to implement Edge Artificial Intelligence on Intel FPGA and Microsoft Azure cloud computing for the prediction of water quality and its evolution, manage an innovative irrigation process, livestock watering points, as well as artisan activities (pottery...).
FPGA-based Irrigation System for Soft Fruit Farms
EM007 »
Prototype of an Intel FPGA-based automatic irrigation system for soft fruit farms in Perthshire, Angus and Fife, Scotland, UK
The smart irrigation system that reduces water use in agricultural areas
EM020 »
Introduction
Since only 3% of the world's water is usable by humans and other living things, it is necessary to be more sensitive in this regard. According to the article published by Worldbank in 2017, it was mentioned that approximately 40% of the world's population lives in water-restricted areas, and it is estimated that approximately 1.8 billion people will live in areas without water by 2025 [1]. Therefore, we should use water resources more efficiently. Abundant use of water in agriculture will create major drought problems in the future. According to the Worldbank, a 60% increase in agriculture is required to feed 9 billion people by 2050, which will increase water use by 15% [1]. According to the CUESA (Center for Urban Education about Sustainable Agriculture), it is mentioned that in order to prevent excessive water use in agriculture, farmers should monitor the weather conditions regularly, while at the same time, the moisture level on the soil and plant should be measured continuously. It is stated that a system to be created by monitoring these values will save water usage [2].
Project Design
In our project, we are planning to develop a system that will reduce water use in an agricultural area. While this system will constantly measure the moisture content in the soil, it will also have a structure that will stop the irrigation system from working in case of rain. We will use the CN-0398 coded soil moisture measurement system to measure the humidity level. In addition, we will check whether it is raining with the HL-83 rain sensor. We plan to reduce unnecessary water use by combining these two systems. After analyzing whether the soil needs water or not, we plan to control the irrigation level by sending the necessary data to the cloud system with the ESP8266 Wi-Fi module in order to analyze the last year’s data. We aim to make a measurement every 10 seconds by the system and to send information about the analysis made according to these measurements to the cloud system in less than 5 seconds. Analyzes will be made with the DE10-Nano Kit.
Expected sustainability results and projected resource savings:
The threat of extinction of the world's waters is a very important problem for sustainability. We think that this project will make significant contributions to sustainability. According to a report published in Nature World News, 30% to 50% water savings were made with the smart irrigation system [3]. We plan to save at least 20% of water in irrigation in agriculture. We believe that thousands of tons of water can be saved if the system is started to be used actively in agricultural areas.
References:
[1] “Water resources management,” World Bank. [Online]. Available: https://www.worldbank.org/en/topic/waterresourcesmanagement. [Accessed: 19-Sep-2021].
[2] “10 ways farmers are saving water,” CUESA, 30-Jun-2021. [Online]. Available: https://cuesa.org/article/10-ways-farmers-are-saving-water. [Accessed: 22-Sep-2021].
[3] M. Brown, “Smart irrigation System 'listens' to Plants cries to reduce water use up to 50%,” Nature World News, 03-Sep-2021. [Online]. Available: https://www.natureworldnews.com/articles/47332/20210903/responsive-drip-irrigation-irrigation-system.htm. [Accessed: 23-Sep-2021].