To minimize the losses that occurred during the storage process of farm produce (vegetables and fruits) by deploying sensor-based IoT technology to monitor and record essential and relevant parameters such as temperature, humidity, freshness indicators, etc.
This project will improve the profitability and customer satisfaction in the fresh produce industry and empower small-scale producers, shippers, and retailers with actionable data to optimize post-harvest inventory rotation and routing decisions.
Project Proposal
1. High-level project introduction and performance expectation
The rate of deterioration of leafy vegetables is determined by the storage environment where temperature and relative humidity are key components. The rate of deterioration of perishables, however, increases two-to threefold with every 10° C increase in temperature. Therefore for most of the perishable commodities, there is a loss of storage potential as handling temperature increases. In addition to deterioration and loss of physical components of quality, vitamin C, which is a major micronutrient in vegetables, is known to decline rapidly after harvest. Loss of vitamin C is often used as an indicator of quality deterioration during post-harvest handling, including transportation, storage, and processing because it is highly susceptible to chemical and enzymatic oxidation and is highly water-soluble.
In this work, it is proposed to use IoT-enabled sensors to monitor the parameters mentioned below to get accurate real-time information on the post-harvest condition of leafy-vegetables throughout distribution. These parameters include temperature, relative humidity, respiration behavior, and freshness, etc. Continuous monitoring of the parameters and analysis of the data thus generated using predictive analytical models (accelerated by implementation on an Intel FPGA) are expected to help identify the variables that limits the shelf-life of leafy vegetables.
Using IoT-based sensors, a large amount of data related to parameters such as temperature, relative humidity, freshness, etc., of leafy vegetables will be generated. The same data will be analyzed using predictive analytics, which will be cumbersome and time-consuming on conventional hardware. Implementing the same analytics on FPGA will accelerate the prediction of the state of the leafy vegetables and thus can provide real-time monitoring of the state of deterioration of produce.Thus implementation of this project on an intel FPGA will benefit us by saving the harvest which will help the rural farmers.
2. Block Diagram
3. Expected sustainability results, projected resource savings
The proposed use of IoT-based sensors combined with real-time tracking helps farmers to reduce the post-harvest losses and increase the monetary benefits per unit product per sale. Sensor data analytics accelerated through implementation on an FPGA help in taking an appropriate decision on the state of the leafy-vegetables within the microclimate created around them during the distribution. Such an approach is expected to be effective for the development of a sustainable post-harvest technology of fresh leafy vegetables that will cater to the needs of a growing population with an extended period of marketability which will also mitigate malnourishment and reduce expenses. The proposed project is expected to allow us to address a majority of the problems related to the supply chain of leafy vegetables while demonstrating the effectiveness of IoT technology combined with FPGA for accelerating analytics. Such an approach is expected to help reduce the post-harvest loss and ensure an efficient supply chain from harvest to plate.
4. Design Introduction
In world of limited sources, there is a need of smart technology where automation can help in addressing the post-harvest loss of perishable leafy vegetables to avoid loss from farm to storage to retailers. In this project, it is proposed to develop a model IoT based smart supply chain with predictive analytical models implemented on Intel FPGA to reduce post-harvest loss and quality deterioration in green leafy vegetables to help link front-end activities of supply chain like local hackers, wholesaler, logistics, retailing etc. with back-end activities of green leafy vegetables production.
India, like many South and South-East Asian Countries, is blessed with a wide array of leafy vegetables of which some are cultivated, many are gathered that are valuable sources of nutrients, especially minerals, vitamins, fibers, protein, and other nutrients which are usually in short supply in daily diet. Green leafy vegetables represent an excellent component of the habitual diet in the tropical country like India. They add variety to a monotonous diet, have an alternative taste, attractive in appearance and contribute a pleasing aroma and natural colour.
Further, consumption of leafy vegetables is one of the nutritional recommendations of the world health organization targeted at preventing and controlling chronic non-communicable diseases, such as obesity, cancer, diabetes mellitus and cardiovascular diseases. However due to urbanization and changes in life style, the consumption of green leafy vegetables is decreasing and the importance of leafy vegetables is underestimated. Lack of attention means that the potential value of leafy vegetables is underexploited. This trend will clearly have detrimental impact on the nutritional status of households and the income, particularly of women farmers who constitute the primary small-scale producers, as well as consumers and seller of these vegetables in India. The scenario thus is restricting development options for women and the rural poor.
Furthermore, the post-harvest loss is a bane of horticulture production in India and many other developing countries. Available data indicates that post-harvest losses as high as 50% have been experienced in Leafy vegetables which are attributed to various biological and environmental factors. This stemmed from the fact that leafy vegetables are classified as highly perishable produce because of their high moisture content (90-96%) and a large surface-to-volume ratio (500-1,000 cm-2cm-3 ). Because of this feature, they usually have high rate of transpiration and Loss of quality and deterioration in harvested leafy vegetables is manifested through loss of freshness as evidenced by wilting, shriveling, and loss of firmness, crispness, and succulence. This results gradually in a loss of chlorophyll (yellowing) and subsequent decay from pathological breakdown. If leafy vegetables loss more than 3% of the original fresh weight, they are rendered unsalable.
5. Functional description and implementation
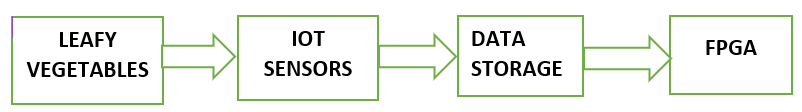
The above block diagram shows the package in which leafy vegetables are transported. Each of the packages has IOT based sensors (as an IOT device with a set of sensors attached to it), these sensors will continuously monitor the parameter already mentioned earlier, and related data are stored locally.
Thus The data collected from different IoT devices is analyzed using a predictive model to access the state of their freshness after implementing the same on an FPGA. So, the FPGA will help in accelerating the data analysis and thus will help in real-time assessment of the freshness of leafy vegetables.
6. Performance metrics, performance to expectation
After testing the prototype model we mentioned above, it is proposed to integrate the IOT device & FPGA on a single board which will be powered by a battery. By the end of this project we propose to build a battery powered embedded device to monitor the state of health of the leafy vegetables.This device is expected to be optimised in terms of the size, power & efficiency.
7. Sustainability results, resource savings achieved
The proposed use of IoT-based sensors combined with real-time tracking helps farmers to reduce the post-harvest losses and increase the monetary benefits per unit product per sale. Sensor data analytics accelerated through implementation on an FPGA help in taking appropriate decision on the state of the leafy-vegetables within the microclimate created around them during the distribution. Such an approach is expected to be effective for the development of a sustainable post-harvest technology of fresh leafy vegetables that will cater to the needs of a growing population with extended period of marketability which will also mitigate malnourishment and reduce the expenses The proposed project is expected to allow us to address a majority of the problems related to supply chain of leafy vegetable while demonstrating the effectiveness of IoT technology combined with FPGA for accelerating the analytics. Such an approach is expected to help reduce the post-harvest loss and ensure efficient supply chain from harvest to plate
8. Conclusion
In this project we proposed a design,develop and demonstrate an Intel FPGA based solution for real time monitoring of the state of freshness of leafy vegetables.This project, if successfull, can be used for any hortyculture produce.
0 Comments
Please login to post a comment.